
Memory Term
& Spec:
-
BBWC and FBWC -
BBWC is a Battery Backed Write Cache Memory. Raid arrays use a
battery backed cache so they
can process data faster than they can write it. Without the battery,
they couldn't do caching without risk of data loss during a power
failure.
There is DRAM memory module which contents are retained as long as
the battery has some juice left.
FBWC is a flash based cache module that does not have the battery
limitation of how long it can retain what is written to the module.
These modules do not require a battery. They have super capacitors
to provide power to flash write cache memory
-
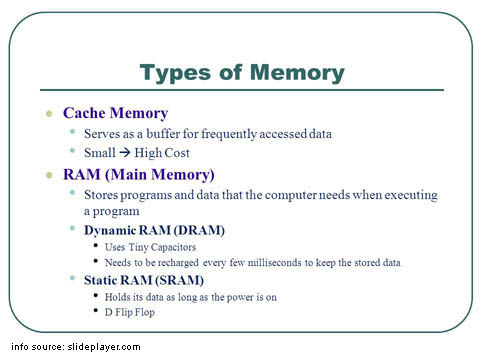
Cache Memory -
Cache memory, also called CPU memory, is random access memory (RAM)
that a computer microprocessor can
access more quickly than it can access regular RAM. This memory is
typically integrated directly with the CPU chip
or placed on a separate chip
that has a separate bus interconnect
with the CPU. The basic purpose of cache memory is to store program instructions that
are frequently re-referenced by software during
operation. Fast access to
these instructions increases the overall speed of the software
program.
-
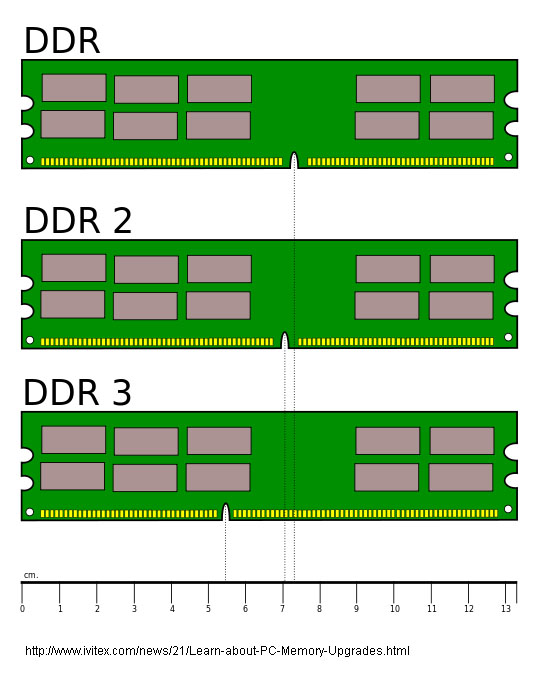
DDR
SDRAM DIMM -
Double data
rate synchronous dynamic random-access memory (DDR SDRAM) is a class
of memory integrated circuits used in computers. DDR SDRAM, also
called DDR1 SDRAM, has been superseded by DDR2 SDRAM, DDR3 SDRAM and DDR4
SDRAM. None of its successors are forward or backward compatiblewith
DDR1 SDRAM, meaning DDR2, DDR3, and DDR4 memory modules will not
work in DDR1-equipped motherboards, and vice versa. Compared to
single data rate (SDR) SDRAM, the DDR SDRAM interface makes higher
transfer rates possible by more strict control of the timing of the
electrical data and clock signals.
-
DDR2 SDRAM DIMM
-
Its primary benefit is the ability to operate the external data bus
twice as fast as DDR SDRAM. This is achieved by improved bus signal.
The prefetch buffer of DDR2 is 4 bit(double of DDR SDRAM). DDR2
memory is at the same internal clock speed (133~200MHz) as DDR, but
the transfer rate of DDR2 can reach 533~800 MT/s with the improved
I/O bus signal. DDR2 533 and DDR2 800 memory types are on the
market.
-
DDR3 SDRAM DIMM
-
DDR3 memory reduces 40% power consumption compared to current DDR2
modules, allowing for lower operating currents and voltages (1.5 V,
compared to DDR2's 1.8 V or DDR's 2.5 V). The transfer rate of DDR3
is 800~1600 MT/s. DDR3's prefetch buffer width is 8 bit, whereas
DDR2's is 4 bit, and DDR's is 2 bit. DDR3 also adds two functions,
such as ASR (Automatic Self-Refresh) and SRT (Self-Refresh
Temperature). They can make the memory control the refresh rate
according to the temperature variation
-
DDR4 SDRAM DIMM -
DDR4 SDRAM provides the lower operating voltage (1.2V) and higher
transfer rate. The transfer rate of DDR4 is 2133~3200 MT/s. DDR4
adds four new Bank Groups technology. Each bank group has the
feature of singlehanded operation. DDR4 can process 4 data within a
clock cycle, so DDR4's efficiency is better than DDR3 obviously.
DDR4 also adds some functions, such as DBI (Data Bus Inversion), CRC
(Cyclic Redundancy Check) and CA parity. They can enhance DDR4
memory's signal integrity, and improve the stability of data
transmission/access.
-
Compare SDRAM, DDR,
DDR2, DDR3, DDR4 -
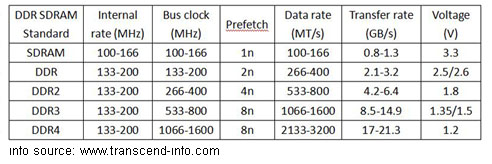
-
ECC -
Error-correcting code memory (ECC
memory)
is a type of computer
data storage that
can detect and correct the most common kinds of internal data
corruption.
ECC memory is used in most computers where data corruption cannot be
tolerated under any circumstances, such as for scientific or
financial computing.
Most non-ECC memory cannot detect errors although some non-ECC
memory with parity support allows detection but not correction.
( info source:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ECC_memory )
-
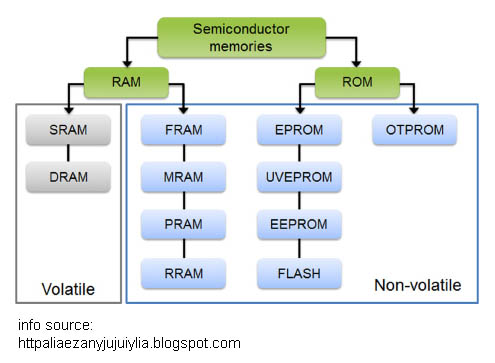
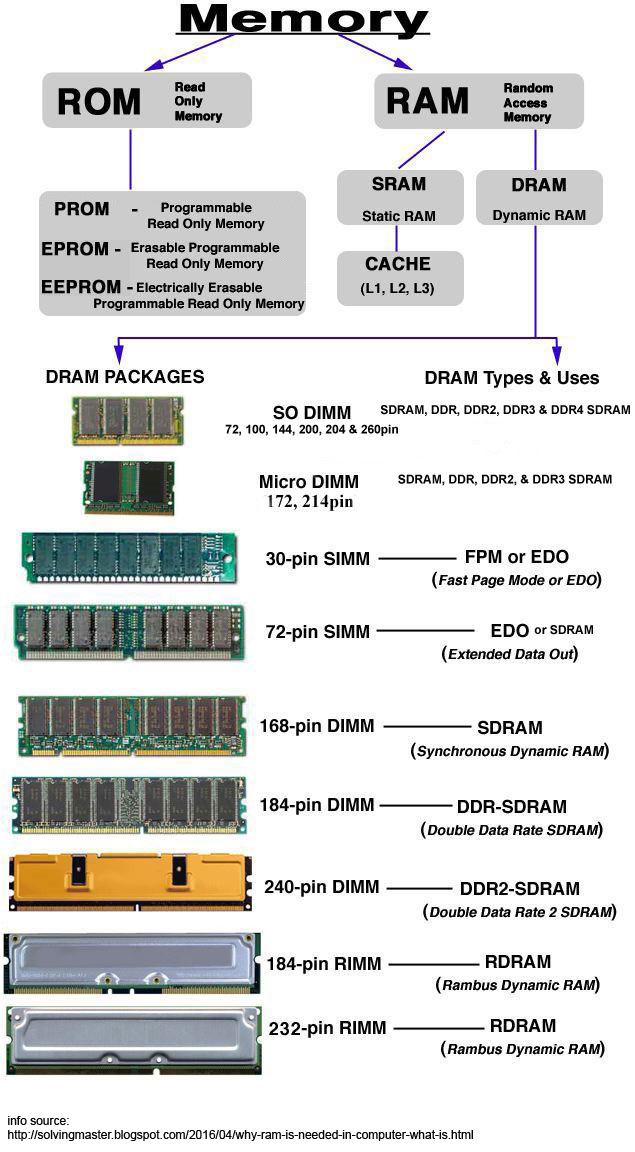
RAM
-
Random Access Memory is a type of computer memory that can be
accessed randomly and holds data temporarily while the CPU is
processes the data. There are two type of RAM categories:
-
DRAM -
Dynamic Random Access Memory. DRAM has to be refreshed thousands
of time per second. DRAM is the most common type of RAM. Both
DRAM & SRAM lose their content when power if turned off.
-
SRAM -
Static Random Access Memory. SRAM does not need to be refreshed
and the access time is about 10 nanoseconds. SRAM is more
expensive. Both DRAM & SRAM lose their content when power if
turned off.
-
SDRAM -
Synchronous DRAM is a generic name for various kinds of DRAM
that are synchronized with the clock speed that the
microprocessor is optimized for. This tends to increase the
number of instructions that the processor can perform in a given
time. As the first RAM to be in sync with the system clock so
that it has 2 notches and 168-pin.
-
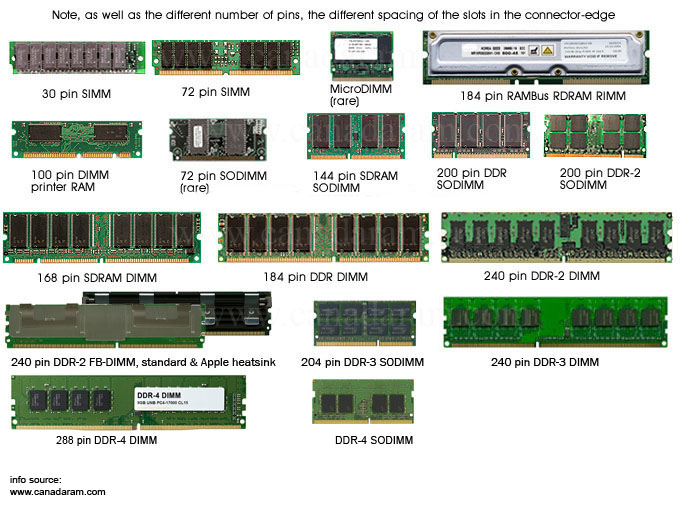
DIMM -
Dual Inline Memory Module
-
Fully Buffered DIMM -
Fully Buffered DIMM (or FB-DIMM)
is a memory technology that can be used to increase reliability and
density of memory systems. Conventionally, data lines from
the memory controller have to be connected to data lines in every DRAM module,
i.e. via multidrop buses. As the memory width increases together
with the access speed, the signal degrades at the interface between
the bus and the device. This limits the speed and memory density, so
FB-DIMMs take a different approach to solve the problem. 240-pin
DDR2 FB-DIMMs are neither mechanically nor electrically compatible
with conventional 240-pin DDR2 DIMMs. As a result, those two DIMM
types are notched differently to prevent using the wrong one.
( info source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fully_Buffered_DIMM,
published by JEDEC Solid State Technology Association )
-
Registered -
Also called Buffered Memory.
-
RIMM -
-
C-RIMM -
-
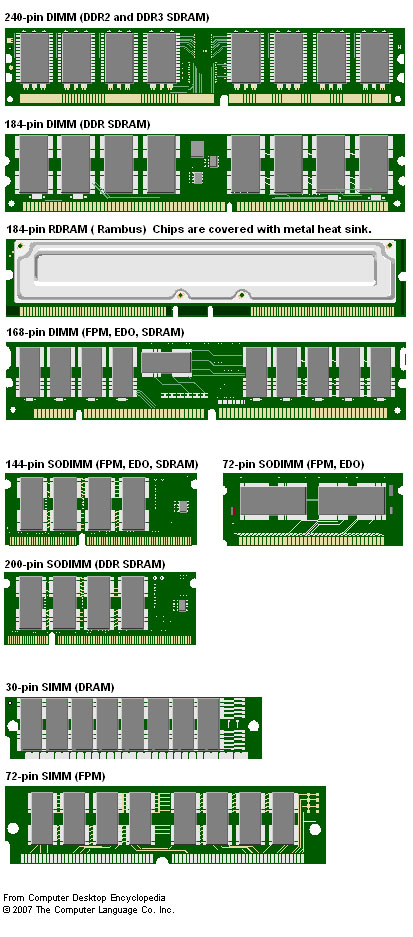
SIMM -
Single Inline Memory Module
-
SIMM-30 -
-
SIMM-72 -
-
FPM -
Fast Page memory, used with 30-pin or 72-pin or some 168-pin
DIMM
-
EDO -
Extended Data Out, improved on FPM, used with 72-pin SIMM or
some 168-pin DIMM
-
BEDO -
Burst EDO, improved on EDO, is rarely used and can be used with
72-pin SIMM or some 168-pin DIMM
-
Single Sided and Double
Sided -
These
are the physical terms describing the arrangement of the chips on
one side or two sides of the memory module. On a double sided module
the chips are on both sides of the module. Single sided modules are
newer with chips that are denser, enabling more capacity. Older
motherboards may not recognize single sided modules
- Size of Memory
-
- mega byte /
megabyte / meg / megs - 64mb, 128mb, 256mb, 512mb, 640mb, 768mb,
1024mb (=1gb)
- giga byte /
gtigabyte / gig / gigs - 1gb, 2gb, 3gb, 4gb, 8gm (=8192mb)
- Standards, Styles,
Speed of RAM Modules -
- DIMM -
- Long / Short
- High Profile / Low
Profile
- Inline / Single Sided
/ Double Sided
- Branded / Generic
- Buffered / Unbuffered
- cl - cas latency
- 144-pin / 168-pin /
184-pin / 200-pin / 240-pin
- 533MHz / 667MHz /
800MHz / 1000MHz / 1066MHz
- PC66 / PC100 / PC133 /
PC1600 / PC1800 / PC2100 / PC2700 / PC3200 / PC3500 / PC3500 /
PC3700 / PC4000 / PC4200 / PC5300 / PC6400 / PC8000 / PC8500
- PC2-
- PC3-
Memory
Pictures:

 |