|
|
|
MMF - Multimode Fiber
Over View An optical fiber is a single, hair-fine filament drawn
from molten silica glass. These fibers are often used as the
transmission medium in high-speed, high-capacity communications systems
that convert information into light, which is then transmitted via fiber
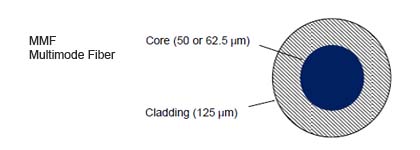
optic cable. Optical fiber is composed of three key elements: Core,
Cladding and Coating. The core is the innermost part of the fiber
through which light pulses are guided. Cladding surrounds the core to
keep light in the center of the fiber. The core and cladding are
inseparable layers of glass. The coating is a layer of polymer that
surrounds the cladding to protect the glass. Optical fiber cable may be Multimode Fiber In general, multimode fiber (MMF) allows a less expensive
system (because the components other than the fiber itself are generally
less expensive), but provides less bandwidth and distance capabilities than
single mode fiber (SMF) systems. However, since the distance and bandwidth
capabilities of MMF are generally sufficient for premises applications, MMF
is the most common type used for backbone and horizontal runs within
buildings and campus environments. Multimode fiber cables include the following: a) 62.5/125 multimode - 62.5 micron core, 125 micron
cladding Typical light source is light emitting diode (LED)
operating at 850 nm or 1300 nm 62.5/125 - Standard b) 50/125 multimode - 50 micron core, 125 micron cladding
c) 50/125 laser optimized multimode - 50 micron core, 125 micron cladding
|